This shows that the production of specific antibodies does not necessarily eliminate sars-cov-2 rapidly, because it can exist with specific antibodies in patients with covid-19 for up to 50 days
Professor Wang peihui of Shandong University and Jiang Xuemei's team of Jinan infectious diseases hospital found that sars-cov-2 can exist in covid-19 patients who have produced virus-specific antibodies for a long time. At present, in two patients, sars-cov-2 can coexist with its specific IgG antibodies for up to 50 days.
At the same time, the study also found a case, in the observation of 66 days, has not produced the specific antibody of sars-cov-2, but at last, the nucleic acid detection of sars-cov-2 turned negative, which shows that the production of specific antibody is not a necessary condition to eliminate sars-cov-2, and also reveals that some individuals may not produce antibodies after infection with sars-cov-2.
The results were published online in medrxiv, a medical preprint, on April 17.

The study involved 26 patients with covid-19 in Jinan infectious disease hospital. According to the clinical characteristics, they were all non critical patients. IgG can indicate a recent or past infection, and it can also indicate the presence of specific antibodies in the body.
Clinical characteristics and IgG antibody production schedule of 26 inpatients with novel coronavirus infection
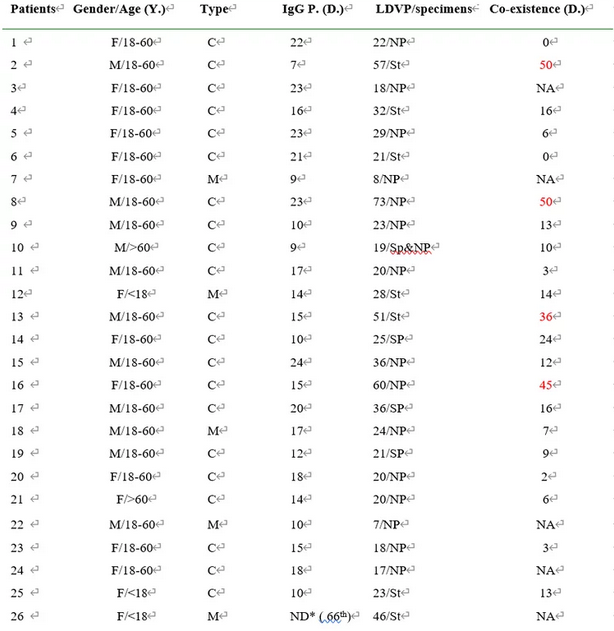
In this study, we found that sars-cov-2 specific IgG antibody can be detected in patients with No.2 disease 7 days later, but the early production of antibody does not mean that sars-cov-2 can be rapidly eliminated. In patients 2 and 8, sars-cov-2 and its specific IgG antibody coexisted for at least 50 days. In addition, sars-cov-2 and its specific IgG antibody were present for at least 36 and 45 days in patients 13 and 16, respectively.
This shows that the production of specific antibodies does not necessarily eliminate sars-cov-2 rapidly, because it can exist with specific antibodies in patients with covid-19 for up to 50 days, which also suggests that the convalescent patients with sars-cov-2 antibodies may have the possibility of secondary infection.
Whether the second infection can be achieved depends on the concentration of sars-cov-2 specific antibody in the convalescent patients. The 66 day observation of patient No. 26 showed that some individuals may not produce sars-cov-2 specific antibody, but they can finally eliminate sars-cov-2.
In this case, natural immunity played an important role in the elimination of sars-cov-2. Therefore, in the treatment of covid-19, the role of natural immune should be concerned, and the use of immunostimulants such as poly (I: C) or cgamp to activate natural immune response may be a potential option.
In conclusion, the study found that sars-cov-2 existed in covid-19 patients who produced specific antibodies for a long time. The production of antibodies does not mean the rapid clearance of sars-cov-2. Therefore, in the process of vaccine development, it is very important to produce antibodies with high specificity and high titer.

